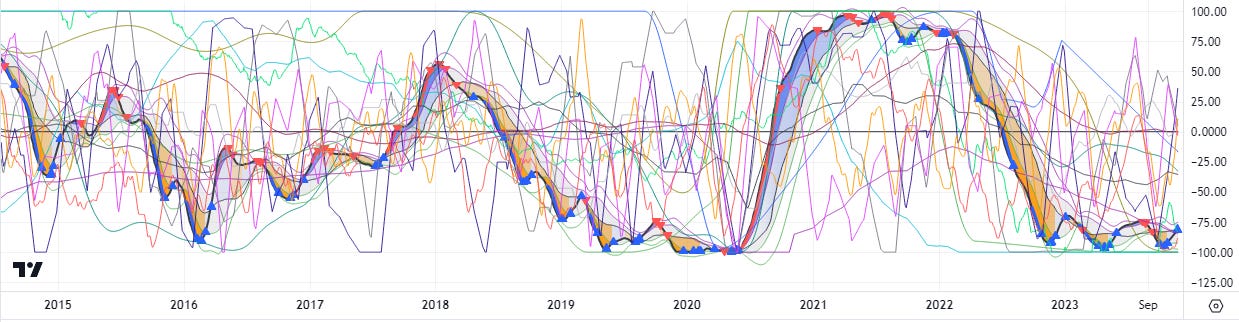
According to my custom Anderson Recession Indicator (ARI) based on 15 economic oscillators, recession began approximately November 2022. The yield curve inverted in April of 2022 and again in June of 2022, and has remained inverted ever since. The ARI has vacillated between -75 and -100 since November, 2022, punctuated by an early 2023 artificial intelligence (AI) bubble, and a banking crisis in March of 2023, and a recent “soft landing” narrative short squeeze, but remains quite anchored in recession territory, much as it did through most of 2019-2020.
Here are the individual ARI components:
[green] United States Money Supply M1, seasonally adjusted — slowing currency supply indicates recession, and this is the first actual contraction in currency supply in about four decades
[olive] velocity of base currency — aggregate currency traded for goods or services (quarterly U.S. GDP x Bureau of Economic Analysis core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index) divided by the base currency supply — increasing currency velocity indicates a liquidity squeeze which portends recession
[teal] Differential between the Effective Federal Funds Rate (EFFR) and the Taylor Rate, which is a forecasting model used to determine what interest rates should be in order to shift the economy toward stable prices and full employment — the closer the Federal Reserve gets EFFR to the Taylor rate, the less the economy is stimulated, and an unstimulated bubble economy is going to crash
[blue] U.S. Treasury 10-year/2-year yield curve cross indicator — triggers on inversions and reversions, which indicate coming recessions
[lime] U.S. Treasury 10-year/2-year yield curve ratio — flat or inverted is more recessionary versus a steep yield curve when the economy is healthy
[aqua] Bureau of Labor Statistics Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers: Energy in U.S. City Average — high energy prices are a leading indicator of recession because energy is an input to everything
[black] Institute for Supply Management (ISM) manufacturing purchasing managers' index (PMI) — under 50 indicates economic contraction
[navy] U.S. consumer credit — falling consumer credit indicates recession
[fuchsia] U.S. durable goods orders excluding defense — slowing durable goods orders indicates recession
[gray] U.S. Census Bureau building permits survey — slowing building permits indicates recession
[silver] Sahm Recession Indicator — three-month moving average of the national U6 unemployment rate relative to its low during the previous 12 months — unemployment is lowest just before a recession
[purple] Deviation of real U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) from the Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) estimate of the output the economy would produce with a high rate of use of its capital and labor resources — negative output gap indicates recession
[maroon] Differential between Bureau of Labor Statistics Import/Export Price Indices — as import prices rise, standard of living declines; as export prices fall, businesses lose money
[orange] McClellan oscillator — NYSE net stocks advancing/declining percentage — even when some headline-grabbing companies are hitting all-time highs, the economic truth is revealed by how the median company is doing
[red] CBOE put/call ratio — the market gets bearish ahead of recessions due to the aggregate earnings outlooks of all of the companies therein, and so put options exceed call options